# How is Dew Point Calculated?
## Understanding Dew Point
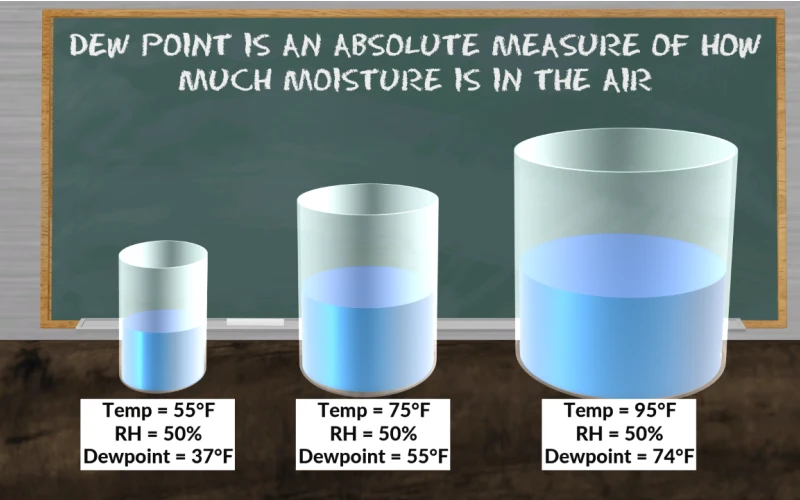
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, fog, or frost. It’s a crucial measurement in meteorology, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. Understanding how dew point is calculated helps predict weather patterns and prevent moisture-related issues in buildings and manufacturing.
## The Basic Formula
The most commonly used formula for calculating dew point is the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– T is the air temperature
– RH is the relative humidity
– a and b are constants (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH/100)
## Step-by-Step Calculation Process
1. Convert temperature to Celsius if necessary
2. Calculate the intermediate value α(T,RH)
3. Plug the values into the dew point formula
4. The result will be in Celsius (convert to other units if needed)
## Practical Example
Let’s calculate the dew point for air at 25°C with 60% relative humidity:
1. α(25,60) = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(0.60) ≈ 1.738 + (-0.511) ≈ 1.227
2. Td = (237.7 × 1.227)/(17.27 – 1.227) ≈ 291.6/16.043 ≈ 18.18°C
## Alternative Methods
While the Magnus formula is widely used, other methods exist:
– The August-Roche-Magnus approximation
– The Arden Buck equation
– Psychrometric charts (graphical method)
– Online calculators and mobile apps
## Factors Affecting Dew Point
Several factors influence dew point calculations:
– Air pressure (though most formulas assume standard pressure)
– The presence of other gases
– Altitude (indirectly through pressure changes)
– The specific constants used in different formula variations
## Applications of Dew Point Calculation
Understanding dew point has numerous practical applications:
– Weather forecasting and analysis
– Preventing condensation in buildings
– Industrial processes requiring precise humidity control
– Agricultural planning and frost prevention
– Aviation safety considerations
## Limitations of Dew Point Calculations
While useful, dew point calculations have some limitations:
– Formulas are approximations with varying accuracy
– Most assume standard atmospheric pressure
– Some don’t account for extreme temperatures well
– Measurement errors in temperature or humidity affect results
## Conclusion
Dew point calculation is a fundamental meteorological process with wide-ranging applications. While the Magnus formula provides a reliable method, understanding its limitations and alternatives ensures accurate results for specific needs. Whether you’re a weather enthusiast, HVAC professional, or industrial engineer, mastering dew point calculations can significantly enhance your work.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated